In micromagnetics, magnetisation dynamics are described using the LLG equation. For non-zero temperature simulations we can use the LLB equation which contains an additional longitudinal susceptibility effective field contribution, as well as a longitudinal damping term. Other equations available in Boris include stochastic versions of these equations, as well as magnetisation dynamics equations complemented by spin-transfer torques and spin-orbit torques. Additionally Boris allows calculations of various spin torques in single and multi-layered geometries using a self-consistent spin transport solver (see Spin Transport).
The LLG equation is given as (for definitions of parameters refer to the manual):
(1) ![]()
In addition to external magnetic fields, a number of contributions can be included in the effective field Heff, the most commonly used are given below.
Demagnetising field:
(2) 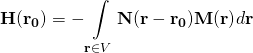
Direct exchange interaction:
(3) ![]()
Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya bulk exchange interaction:
(4) ![]()
Interfacial Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya exchange interaction:
(5) ![]()
Surface exchange in multi-layered geometries:
(6) ![]()
Uniaxial magneto-crystalline anisotropy:
(7) ![]()
Cubic magneto-crystalline anisotropy:
(8) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \begin{equation*} \begin{align*}\mathbf{H} = -\frac{2K_1}{\mu_0 M_s} [\mathbf{e_1} \alpha (\beta ^2 + \gamma ^2) + \mathbf{e_2} \beta (\alpha ^2 + \gamma ^2) + \mathbf{e_3} \gamma (\alpha ^2 + \beta ^2) ] \\ -\frac{2K_2}{\mu_0 M_s} [\mathbf{e_1}\alpha \beta^2\gamma^2+ \mathbf{e_2}\alpha^2\beta\gamma^2+ \mathbf{e_3}\alpha^2\beta^2\gamma] \end{align*} \end{equation*}](http://www.boris-spintronics.uk/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-8025d70d35393a7478496d49134f8d93_l3.png)